What Is Preventive Maintenance?

Most facilities have several pieces of equipment and machinery that are critical for day-to-day operations. Maintenance can be complex, and experiencing an unexpected machine breakdown can delay production and waste time and money.
Planned preventive maintenance is regular and routine equipment maintenance to keep it running at its optimal level. Preventive maintenance prevents unplanned, expensive downtime by taking care of problems when they are smaller and more manageable or before they ever happen. Another critical component is keeping records of machine maintenance to identify patterns to create a strategic maintenance schedule.
What Are the Types of Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance’s function is to prevent equipment breakdown by anticipating the need for it. This prevention requires three types of tasks.
- Mandatory tasks: These tasks are safety-critical and completed as soon as the need arises. Non-mandatory tasks take place at a later time.
- Pyramiding tasks: Pyramiding tasks are when maintenance does not happen by a due date, so it overlaps with a future need.
- Inspection tasks: These tasks require investigating a suspected problem.
Anticipating equipment needs involves a few types of preventive maintenance.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses temperature or vibration sensors to capture information about equipment. When these sensors detect specific conditions, they’ll trigger a work order or notification to alert you that an inspection or upgrade is necessary. It involves monitoring the machine’s status by tracking performance and detecting issues that could cause a more complex problem.
Based on your equipment’s history, you can use predictive maintenance to anticipate when a machine will need repairs and schedule downtime to prevent a system shutdown.
Prescriptive Maintenance

Prescriptive maintenance uses artificial intelligence, machine learning and advanced analytics to predict and act on maintenance needs. It recommends needed repairs and follows up by producing a work order and overseeing the process. This preventive maintenance is the most technologically advanced type.
FUJIFILM AI technology can highlight and extract discontinuity information and supply engineers with data to analyze potential defects.
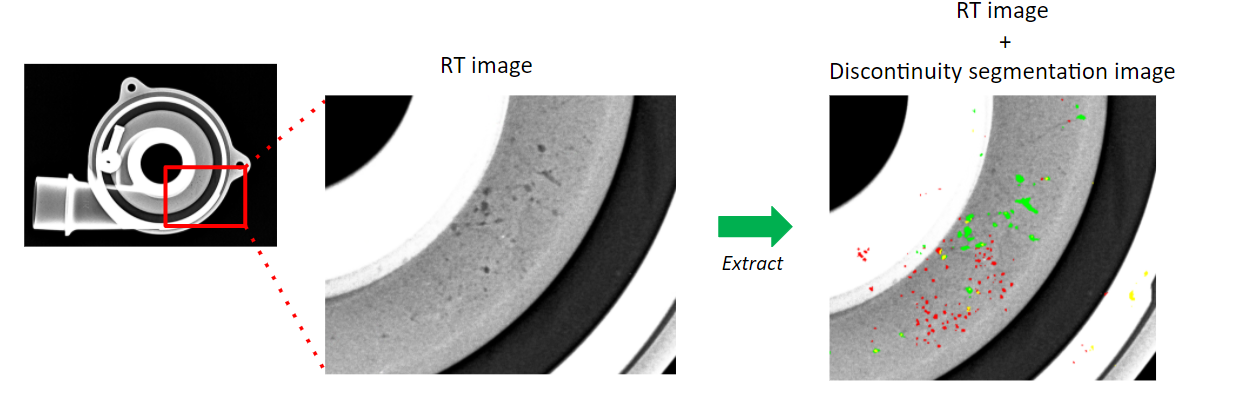

The extracted discontinuity information can be displayed within our VU software to highlight potential defects in the future.
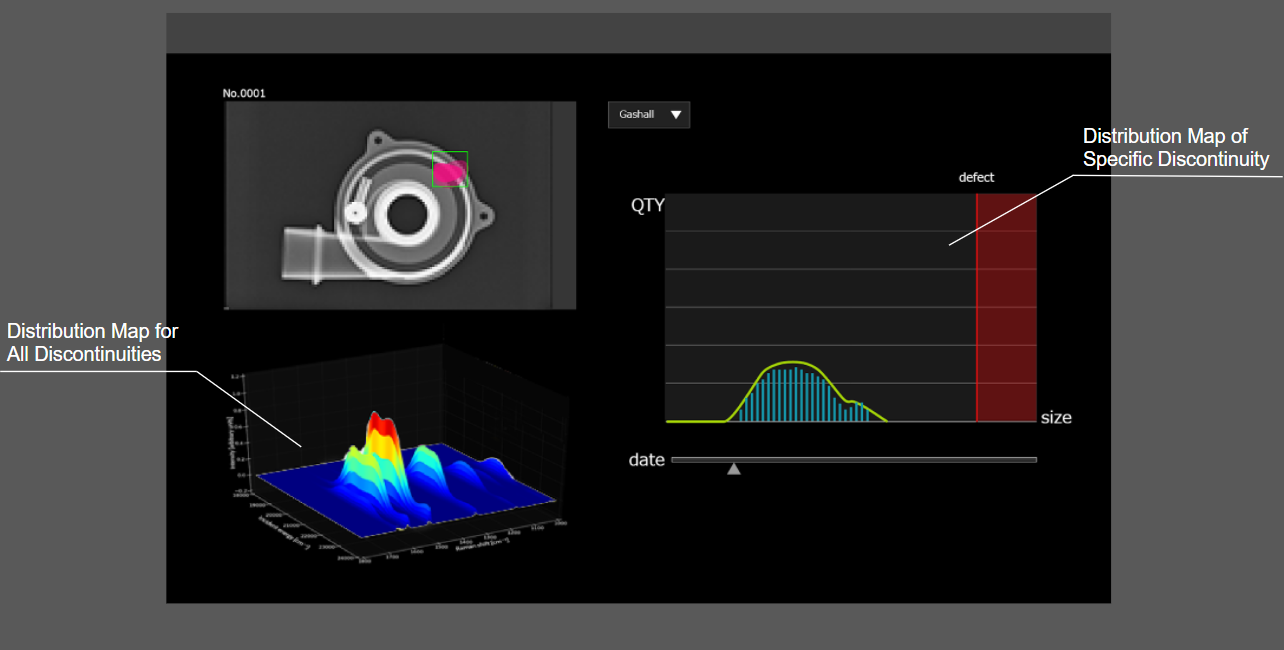
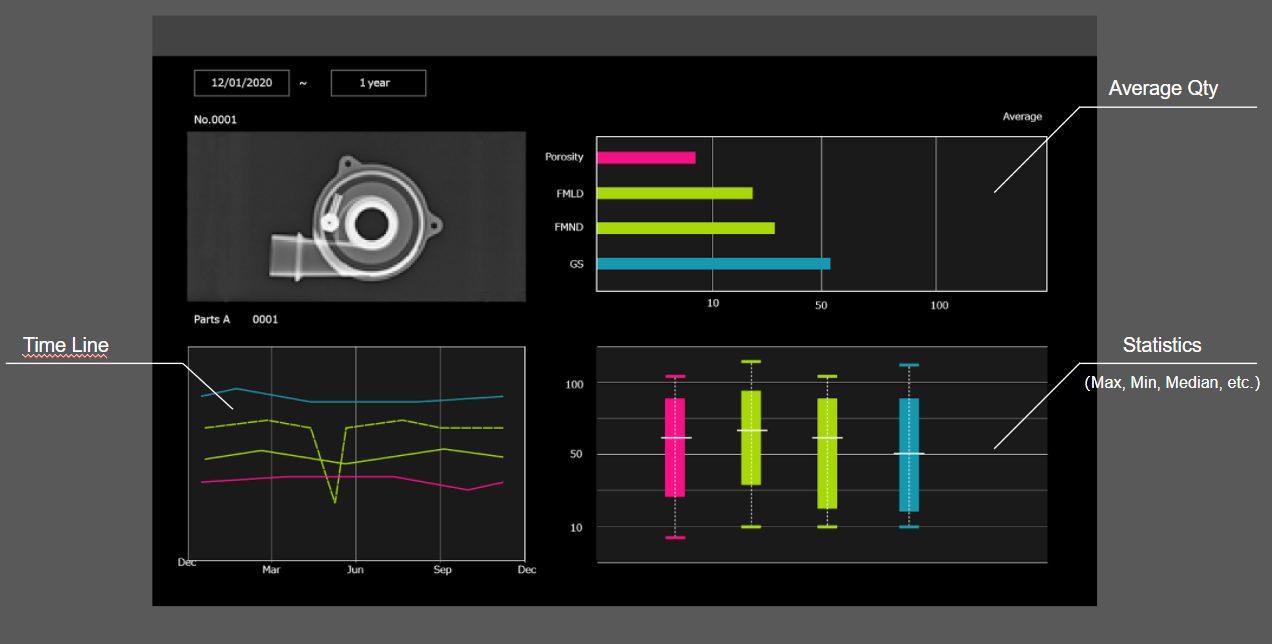
Usage-Based Maintenance
Usage is the operating hours, production cycle and equipment monitors for machinery and equipment. These factors show how much use the equipment gets, and you can rely on this information to determine your needs. Usage-based maintenance requires monitoring these stats and doing the necessary upkeep when it reaches a specific level.
Changing the oil in your vehicle after 5,000 to 7,000 miles and inspecting a machine after it’s reached a specific number of operating hours are examples of usage-based maintenance.
Time-Based Maintenance
Time-based maintenance creates a monthly or annual inspection and cleaning schedule based on manufacturer recommendations. When creating your plan, consider the utilities, technology, tools and equipment your business relies on. Check essential equipment regularly and less crucial equipment more infrequently. Keep notes about your maintenance for all equipment to determine which tools need the most care.
Examples of time-based maintenance include servicing your air conditioner two months before summer or cleaning the vents twice a year to comply with health standards.
When Is It Best to Use Preventive Maintenance?
Your preventive maintenance plan will vary for each piece of equipment and its operations. The best time to use preventive maintenance depends on industry standards and manufacturer recommendations. These specify the required inspection or upkeep for each problem the machine may have.
You will need to accurately record your inspections and maintenance services and use this information to create a preventive maintenance schedule. If you follow these standards in your plan, you will be proactive instead of reactive.
Industries That Benefit From Preventive Maintenance
Here are the industries that stand the most to gain from having a preventive maintenance plan.
- Manufacturing: Factory equipment can be custom-made and costly. Preventive maintenance helps businesses maintain their investment to avoid production delays.
- Fleet management: Vehicle problems can disrupt business since other companies rely on these vehicles to transport their goods. Preventive maintenance can catch these problems before failure and keep business moving like usual.
- Hospitality and restaurants: Hospitality businesses, especially restaurants, have a lot of valuable equipment to maintain. Since malfunctioning equipment can lose thousands of dollars in profit, preventive maintenance helps keep this equipment operational, so businesses can operate without interruption.
- Oil and gas: Equipment safety is crucial in the oil and gas industry, where a malfunction could cause environmental damage. Preventive maintenance can monitor equipment’s condition remotely, leading to cost savings on inspections and prevention of severe accidents.
Suitable Applications of Preventive Maintenance
A good preventive maintenance strategy is to do it for suitable applications only. These are equipment and machines that meet these conditions.
- It is critical to health and safety, operations or production in your facility.
- Routine maintenance can prevent failures.
- Its chances of failure increase with time or use.
Some assets are not ideal for preventive maintenance. Attempting to get ahead and avoid premature breakdowns with these machines would be a waste of time and resources. Do not use preventive maintenance on assets that meet these conditions:
- It does not serve a critical function.
- The cost of repairs is higher than the cost of running it to failure.
- It fails randomly in ways that do not relate to maintenance, such as circuit boards.
Tips for Scheduling Preventive Maintenance

When deciding when to do preventive maintenance, ensure you’re not overdoing it. Proactive upkeep aims to maintain machines, and the best time to do so is when the benefits outweigh the risks and costs. Follow these tips to decide if preventive action is necessary.
- Check the work history: Look at the machine’s work history before scheduling maintenance. Preventive maintenance is likely unnecessary if it hasn’t been too long since the previous test, update or improvement.
- Consider the benefits: It may not be necessary to do preventive maintenance, even if an opportunity comes up. If you are overzealous, you can waste time and money.
- Determine the machine’s importance: Direct most of your preventive maintenance measures toward your critical equipment, then work your way down.
- Keep simple preventive measures in check: Don’t overdo your preventive maintenance. For example, over-lubricating machinery is unnecessary. Actions like this waste time and materials and could damage machinery that previously had no issues.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
A preventive maintenance program provides several cost, error and health and safety benefits for all industries. The advantages include the following.
- Staying ahead of problems: Preventive maintenance’s purpose is to stay ahead of problems by addressing them before they occur.
- Improved safety: Equipment failure can be dangerous because it can injure workers and risk workers’ compensation and liability lawsuits. Preventive maintenance catches problems early on and corrects them before anyone gets hurt.
- Increased productivity: When machinery is running poorly, it limits how productive your workers can be. Downtime and troubleshooting prevent employees from making progress with their work. With preventive maintenance, equipment will have less downtime, and workers will have more uptime.
- Improved reliability: Inconsistency with your machine’s performance takes a toll on your efficiency. With preventive maintenance, you can count on the machine to run whenever you need it, so it’s more reliable.
- Lengthened equipment lifespan: Equipment that runs well lasts longer. Failed parts require an expensive repair, and they reduce your equipment’s life. Using preventive maintenance to keep your equipment running well will prolong its usable lifespan.
- Reduced costs: Running equipment until it fails generally costs more than preventive maintenance measures because unexpected repairs and shutdowns are expensive. Preventive maintenance helps you understand your machine’s requirements, so you can schedule repairs and replacements before it fails.
- Lower energy consumption: Poorly maintained equipment runs inefficiently because it consumes more energy. Preventive maintenance keeps equipment running well, so it uses less energy, which decreases utility bills and your environmental impact.
- Fewer operational errors: When equipment is working incorrectly, it’s more liable to make mistakes. Preventive maintenance reduces these errors to save time and materials.
- Eliminated overtime costs: Preventive maintenance makes the equipment more reliable, so it will run as expected during the workday. By preventing unexpected breakdowns, your employees won’t have to work overtime to make up for the time lost during their scheduled hours. When your workers stick to their schedules, you won’t need to pay for overtime.
Features and Benefits of Preventive Maintenance Software
Another benefit of preventive maintenance is using software to make your workflow easier. Preventive maintenance software allows users to:
- Have one place for all the preventive maintenance work orders and records.
- Create and schedule work orders.
- Modify work orders that are in progress or complete.
- Track work orders from start to finish.
- Use data to identify trends for issue causes, operational downtime and repair costs.
- Access and allocate resources strategically.
- Alert maintenance crew about job due dates.
This level of oversight makes preventive maintenance quicker and more effective and boosts your preventive maintenance program’s benefits. It also takes care of the administrative tasks, so technicians can focus on making repairs.
Disadvantages of Preventive Maintenance

Though a preventive maintenance program has many advantages, there are a few drawbacks to consider.
- Extra cost: Though preventive maintenance creates cost savings from equipment repairs, starting a preventive maintenance schedule at your facility can have a high cost. The initial expense means that many companies only do preventive maintenance for critical machines and not all equipment. Preventive maintenance software can be expensive and require hiring external experts, but this is becoming less of a problem with new, affordable options entering the market.
- Difficult to organize: Preventive maintenance can seem daunting for facilities with hundreds or thousands of machines, especially when your company doesn’t have records and statistics to reference. Software can help you stay organized by reminding technicians about jobs they need to complete and eliminating the need for paper records. With proper planning, your company can implement an effective preventive maintenance program.
- Resource-intensive: Running a preventive maintenance program requires more staff, parts and time than other types of upkeep. Some companies may not have the means to spare. One way businesses can take advantage of preventive maintenance without overextending themselves is by focusing preventive maintenance efforts on critical machines only.
- Time-consuming: Due to the number of resources required to run a preventive maintenance program, companies may think it is not worth it. Regular, thorough equipment inspections can take a lot of time and may tempt technicians to skip the job, especially if they have other responsibilities to take care of.
- Excessive efforts: You may have the urge to go overboard, but too much preventive maintenance is not beneficial. It wastes money, time and resources with no benefits gained. An efficient preventive maintenance program requires identifying the “Goldilocks” frequency that is neither too little or too much.
Preventive vs. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is an advanced option that requires technology. Sensor data from the machine connects to your data history program, and it analyzes information to determine if the machine has met specific conditions. The program can predict when a part or machine might break down, so technicians can make the repair before failure occurs. Predictive maintenance reduces the number of preventive maintenance tasks.
While predictive maintenance can be more complex, time-consuming and costly than preventive maintenance, a well-designed predictive maintenance system helps ongoing equipment maintenance and helps companies make informed financial decisions. Maintenance only happens when it’s essential, so there are no wasted resources. According to industry analysts, predictive maintenance and the Internet of Things will generate an economic impact of $1.2 to $3.7 trillion in 2025.
Preventive vs. Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance involves repairing parts and equipment after the part has broken down or the machine has run to the point of failure. This method pushes parts, machines and production to their maximum output. Unlike preventive maintenance, reactive maintenance does not require planning. The disadvantages of this method are as follows.
- High costs: Repairing the asset after failure can be expensive and might cost more than its production value.
- Extensive damage: While running machines to failure, parts can vibrate, overheat and break, which can damage the equipment further and create more repair expenses.
- Incorrect repairs: When making repairs for a reactive maintenance program, technicians may focus on treating the symptom rather than the problem. If a specific part needs frequent replacement, the underlying issue may be with another area of the machine and not that component.
Choose FUJIFILM North America Corporation for Your NDT Needs
Fujifilm uses high-quality imaging products to provide non-destructive testing. Your company can inspect parts to meet your specifications without damaging any components. We help companies transition to Industry 4.0 and new products and services by streamlining the inspection process.
Contact us to learn more about our NDT services.











